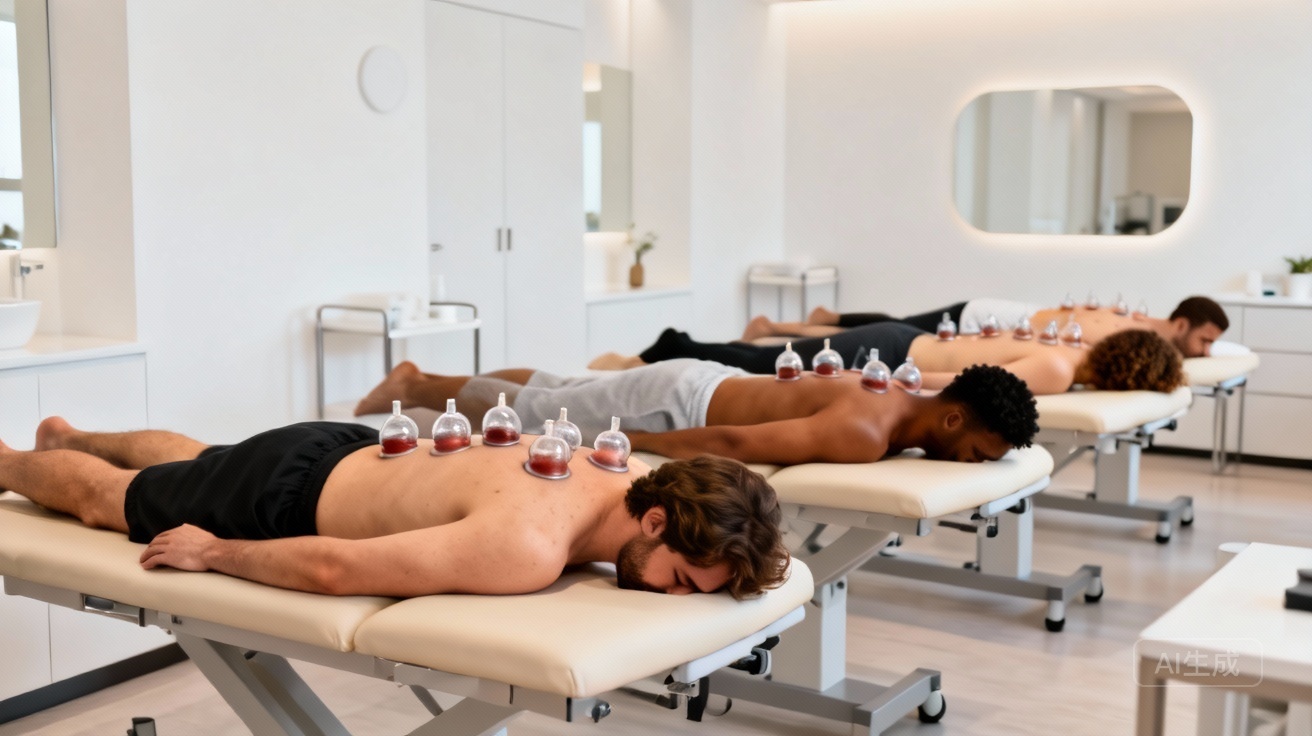
Safely Prepare for Cupping: Expert Care is Crucial!
Choose Wisely: Ensure Expert Hands
Your cupping experience starts with selecting the right person. Always ensure a qualified, properly trained practitioner performs your session. Their expertise guarantees a safe and effective procedure. Additionally, rigorous sterilization of all equipment is non-negotiable. This critical step actively prevents the spread of infection. Remember, cleanliness directly impacts your healing. A systematic review highlights the importance of professional application and hygienic practices to minimize adverse events in cupping therapy (PMID: 26867744).Mindfully Approach Cupping: Ensure Your Cupping Therapy Safety!
Assess Your Health: Prevent Complications
Not everyone is a suitable candidate for cupping therapy. Certain health conditions make it unsafe for you. For instance, avoid cupping on broken skin or infected areas. This prevents further irritation and serious complications. People with severe varicose veins should also abstain. This avoids potential damage to fragile blood vessels.Check Your Medications: Stay Risk-Free
Individuals with blood disorders or those on anticoagulant medications face higher risks. Cupping could lead to excessive bruising or bleeding. Acute high fever or severe heart and lung conditions also contraindicate cupping. It might worsen your existing health issues. Pregnant individuals should avoid cupping on the abdomen and lower back. Young children and very weak individuals require extreme caution. Their delicate bodies are more sensitive to the therapy. Learn more about Cupping Therapy techniques and benefits here. Always consult a healthcare professional before undergoing cupping, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are on medication, as highlighted in comprehensive reviews of cupping therapy safety (PMID: 26084224).Stay Aware During Cupping: Listen to Your Body Immediately!
Monitor Suction: Optimize Your Session
During the session, your practitioner carefully controls the suction strength. They also manage the duration of each cup. Typically, cups remain in place for 5 to 15 minutes. This timeframe helps achieve therapeutic effects without over-stressing your skin. It also prevents any stagnation, which in TCM, is like a traffic jam in your body, where energy and blood flow get stuck. Understand Qi and Blood circulation in TCM.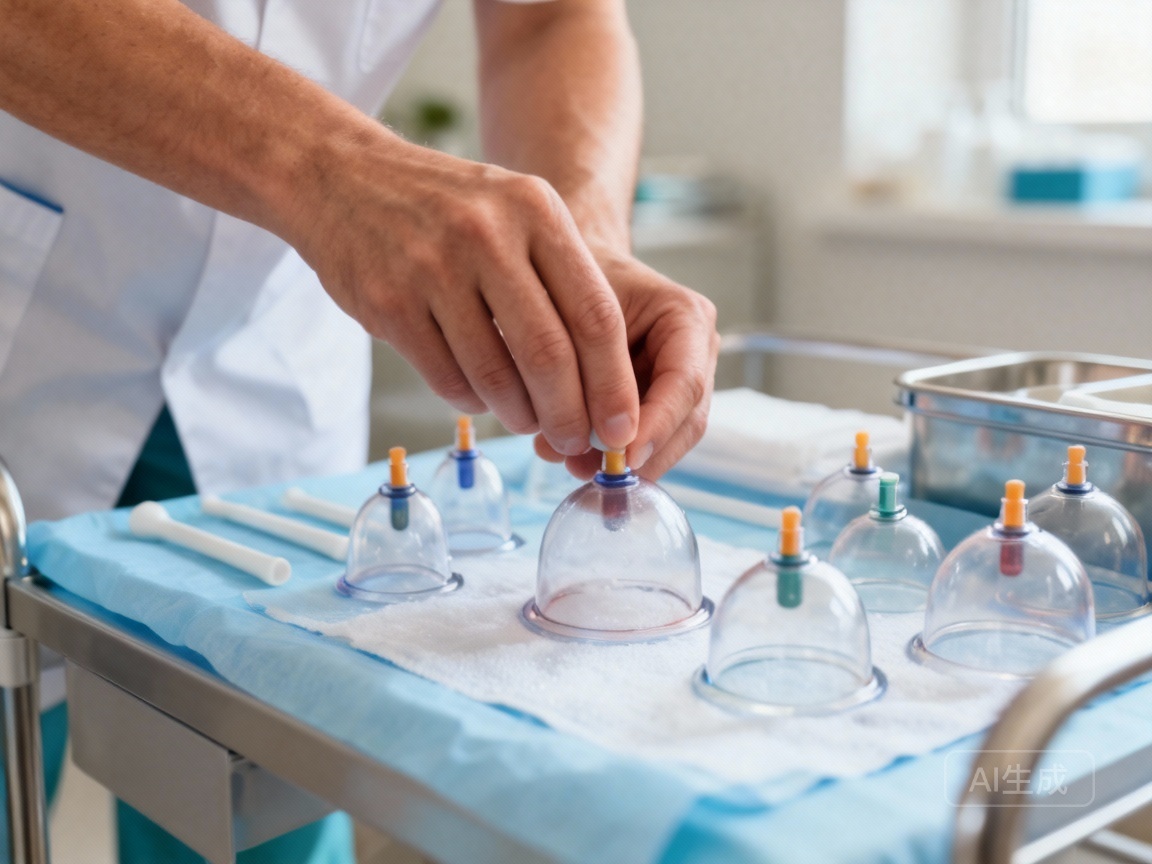
Respond Promptly: Address Discomfort Fast
Your comfort is paramount throughout the entire session. If you experience severe pain, tell your practitioner immediately. The same applies to developing blisters, significant bleeding, or dizziness. Additionally, report any difficulty breathing right away. In such cases, the cups must be removed without delay. Prompt action prevents adverse reactions from escalating further.Post-Cupping Bliss: Carefully Nurture Your Healing Skin!
Practice Aftercare: Support Recovery Smoothly
After your cupping session, proper aftercare is crucial for recovery. Post-cupping care is a critical aspect of overall cupping therapy safety. Keep the treated area clean and warm. Avoid exposing it to extreme hot or cold temperatures. Refrain from scratching the marks, even if they itch slightly. Also, it’s best to avoid alcohol consumption for a day or two. These simple steps support faster healing. Adhering to post-cupping care instructions is vital for preventing complications, a factor often emphasized in studies examining cupping therapy's efficacy and safety (PMID: 30046559). Explore more tips for healthy living and wellness practices.When to Act: Uphold Your Cupping Therapy Safety Seriously!
Seek Help: Don't Ignore Persistent Symptoms
While cupping is generally safe, unexpected reactions can sometimes occur. If you notice persistent redness, swelling, or pus at the cupping sites, seek medical attention. A fever or general feeling of unwellness also warrants a doctor's visit. These symptoms could indicate an infection or a more serious issue. Trust your instincts and consult a healthcare professional immediately. Always prioritize your cupping therapy safety, ensuring you avoid adverse reactions, potential risks, and unwanted side effects. Adhering to these guidelines helps prevent skin irritation, infection concerns, bleeding complications, and ensures a positive healing experience. Following these guidelines will vastly improve your overall cupping therapy safety and enjoyment.Quick Self-Check & Self-Rescue Guide (3-Second Scan, 30-Second Action)
If you notice a sudden sharp pain or intense discomfort during cupping → Immediately tell your practitioner to remove the cups.
If you develop persistent redness, swelling, or pus at the cupping sites after your session → Immediately consult a healthcare professional.
If you feel dizzy or lightheaded during cupping → Immediately inform your practitioner and ask for the cups to be removed, then rest and drink some water.
Medical Disclaimer:This article is for educational use only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.